Periodontal Disease Treatment (Gum Disease)
Gum disease is a serious condition that affects people from all walks of life. We offer gum disease treatment to enhance your dental health.
What is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, periodontitis, or gum disease is an infection affecting the gums and bone surrounding your teeth. This infection occurs when food particles and plaque accumulate between the gums and teeth, leading to inflammation and infection. Periodontal disease is a significant oral health issue that impacts many individuals and stems from bacterial accumulation on the teeth.
Gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease, is characterized by slight redness, swelling, and sometimes minor bleeding of the gums. Without appropriate treatment, gingivitis can escalate into periodontal disease, a more severe infection that may cause irreversible damage to the gums and bone structures supporting the teeth.
It’s estimated that nearly half of all adults experience some form of periodontitis. This condition develops when the gums are continually exposed to harmful bacteria, tartar, and plaque, often due to inadequate flossing and debris buildup between the teeth. This can progress to significant bone deterioration and tooth loss if not addressed.
We provide treatments for gum disease right here in Chelmsford, MA. To learn more about how we can help you maintain healthy gums, please schedule a consultation online using the provided link or contact our office directly today.
-
How does a dentist identify if gum disease is present?
Early detection of gum disease is key to preventing tooth and bone loss. To assess whether you have periodontitis and the extent of the condition, we will:
- Review your medical history: Certain factors such as genetics, specific medications, or smoking can heighten your risk of developing gum disease.
- Examine your teeth and gums: Signs like significant plaque or tartar accumulation and bleeding gums are common indicators of gum disease.
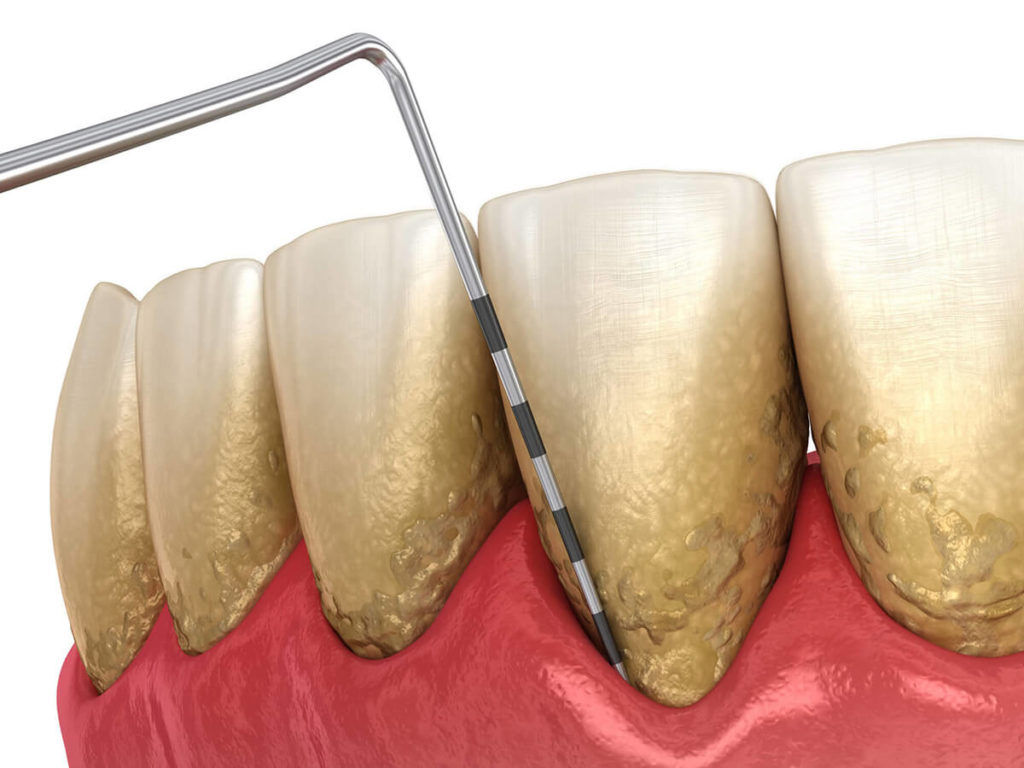
- Measure gum pocket depth: By inserting a dental probe between your teeth and gums at various points in your mouth, we measure the depth of the gum pockets.
- A depth of 1-3 mm indicates healthy gums.
- A depth of 3-5 mm suggests early or mild periodontitis.
- A depth of 5-7 mm indicates moderate periodontitis.
- A depth of 7-10 mm points to advanced periodontitis.
- Take dental X-rays: X-rays help detect any bone loss in areas where the gum pockets are deeper.
These steps are crucial for diagnosing and formulating an effective treatment plan for periodontitis.
-
How much does periodontal treatment cost?
If you have periodontal disease, it is crucial that you keep up on your periodontal maintenance to prevent any further damage to your teeth and gums. Our office strives to provide the best care, at the most affordable rates. Out-of-pocket cost for any procedure depends on your insurance coverage at the time of the procedure.
Periodontal Maintenance in Chelmsford, MA: $201
See All Office Fees -
What causes periodontal disease or gum disease?
Our mouths provide a home to millions of bacteria, both beneficial and harmful. Bacteria form a sticky substance, plaque, that adheres to the teeth. Brushing and flossing aim at removing plaque before it mineralizes into tartar. Tartar becomes a colony for more bacteria and adds to their population, pumping out toxins into the gums.
Gums react to this bacterial invasion with an inflammatory response under the direction of the immune system. Around the base of each tooth, a small collar of gum tissue exists that forms a small crevice or pocket. This warm, dark environment provides a perfect habitat for deeper tartar and bacterial penetration, with their toxins seeping into the base of the collar.
Early inflammation results in bleeding gums, known as gingivitis. Bacteria left untreated and undisturbed successfully create a chronic infection in the gum collar. In many cases, the bone begins to deteriorate around the teeth as the bacteria burrow deeper into the gums. While gums may be slightly tender at this stage, there’s generally minimal discomfort as the bone dissolves.
More than 50% of the bone around your teeth can disappear before any signs of looseness or pain begin to appear. The bone around teeth never regenerates, so this loss becomes permanent and harder to control as the bacteria hide deeper into the gums. Untreated gum disease leads to abscesses and generalized tooth loss in many advanced cases.
-
How do I prevent periodontal disease or gum disease?
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is primarily caused by plaque buildup, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. When plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar (calculus), which is much more difficult to remove and provides a further breeding ground for bacteria. Here are the main factors that contribute to the development of periodontal disease:
- Plaque Buildup: The primary cause of gum disease is plaque, which can harden into tartar if not regularly removed. The bacteria in plaque produce toxins that irritate the gum tissue, leading to inflammation and various gum disease.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing make it easier for plaque to build up and turn into tartar, setting the stage for gum disease.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products significantly increases the risk of periodontal disease, as tobacco interferes with gum tissue cells’ ability to function and recover from damage.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are genetically more susceptible to gum disease, even if they maintain good oral hygiene.
- Hormonal Changes: Changes in hormone levels during puberty, pregnancy, menopause, and monthly menstruation can make gums more sensitive and more vulnerable to gum disease.
- Poor Nutrition: A diet lacking in important nutrients can impair the body’s immune system, making it harder to fight off infections, including periodontal infections.
- Diseases: Illnesses that affect the immune system, such as diabetes and HIV/AIDS, can interfere with the condition of the gums. In addition, diseases like diabetes can make an individual more susceptible to infections, including periodontal diseases.
- Medications: Certain medications that cause dry mouth or gum changes can increase the risk of gum disease. Medications such as anticonvulsants, calcium channel blockers, and immunosuppressants can affect oral health.
- Stress: Chronic stress can make it difficult for the body to fight off infection, including periodontal disease.
- Misaligned or Crowded Teeth, Braces or Bridgework: Anything that makes it more difficult to brush or floss your teeth is likely to enhance plaque and tartar formation, increasing the risk of periodontal disease.
Addressing these factors through proper oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and making lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease.
What are you waiting for?
At Drum Hill Dental, we believe in providing the best dental care at the most affordable prices. Make your next appointment using our easy online scheduling tool, contact our office if you have any questions, or explore all of the dental services we provide.

